
Global supply-chain management is the process of distributing goods and services within a global company's network. The principle behind this concept is to maximize profit, while minimizing waste. Although there are many advantages to this distribution model, there are also some drawbacks. Let's look at some of these issues. Read on to learn more about the benefits of global supply chain management. We'll also be discussing some of the difficulties associated with global Supply Chain Management.
Resilience
To be a successful global supply chain manager it is important to develop a strategy that promotes resilience. You can increase the resilience of your supply chain by redesigning it, making redundancies and using multiple sourcing. Although supply chains may seem rigid in the short term they can become more resilient with constant vigilance. Cin7 is an inventory management software company that has provided various educational materials as well as advice to its customers.
Information sharing
Although the role information sharing plays in global supply chains management may seem vague, it is crucial to the survival companies. This study explores the ways in which information sharing can benefit multiple parties within a supply chain. Information sharing offers many benefits, which may vary depending on the type of information. Information is generally valued differently depending on who it is shared with. Here are some examples to illustrate the benefits of information for supply chains.

Quality management
Quality issues are a key component of any supply chain. It is crucial for companies to ensure product quality. However it is equally important that secondary issues are addressed and supply chain risk managed. This article will discuss the role of quality management in global supply chain management. It will also show how current business systems can fail this challenge. Let's look at some of the ways companies can overcome these problems and implement better quality management practices.
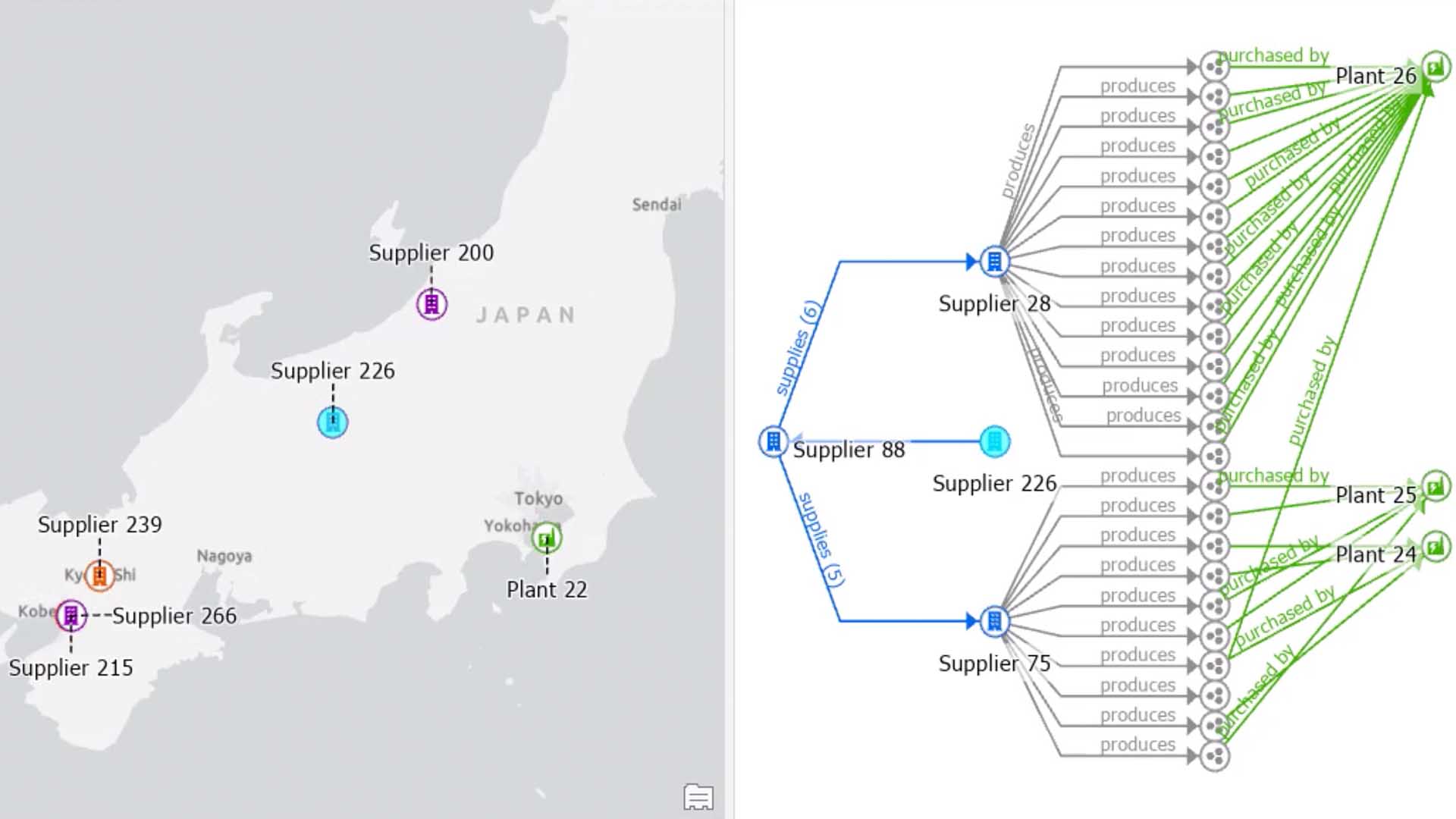
Logistics links
As consumers' demands and preferences continue to evolve, so do the needs of the business. Global supply chains are a complex network of individuals, companies, and suppliers who work together to deliver goods to the correct place and at the right time. Logistics plays a vital role in global logistics management. It allows companies to lower their costs while improving their performance. In addition to businesses, supply chains include vendors, producers, warehouses, transportation companies, distribution centers, retailers, and more.
COVID-19 pandemic
Global supply chains management is critical due to the recent outbreak of COVID-19. Global supply chains are vital to response efforts, supplying essential supplies in a timely manner. But other issues such as the Chinese lockdown and uncertainty in the global economy have made it difficult for the global supply to remain open. This pandemic is proving to be a test of supply chain resilience and flexibility. Companies will be judged on not only their response but also their corporate values after this crisis.
Impact on the economy
Global supply chain management is vital for the global economy. As manufacturers move to JIT (just as-needed) production, they will become more dependent upon one source for vital supplies. JIT production models do have one major problem: they leave companies open for disruptions in their supply networks. Recent research has shown that half of the executives plan to cut production from China and that one-third plan on de-emphasizing JIT manufacturing.
Chances for advancement
Global supply chain management oversees all aspects of an organization's international procurement strategy. They are responsible for the management of inventory and will work closely with suppliers to ensure that high-quality products are produced. They keep track of the supply chain performance, analyze data and make recommendations. This role is also dependent on collaboration with other departments. Below are some career options available to people with this experience. All of them offer valuable career benefits.
FAQ
What is meant by manufacturing industries?
Manufacturing Industries refers to businesses that manufacture products. Consumers are those who purchase these products. This is accomplished by using a variety of processes, including production, distribution and retailing. These companies produce goods using raw materials and other equipment. This covers all types of manufactured goods including clothing, food, building supplies and furniture, as well as electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles and pharmaceuticals.
Why automate your warehouse?
Automation has become increasingly important in modern warehousing. With the rise of ecommerce, there is a greater demand for faster delivery times as well as more efficient processes.
Warehouses must be able to quickly adapt to changing demands. Technology investment is necessary to enable warehouses to respond quickly to changing demands. Automating warehouses is a great way to save money. These are just a few reasons to invest in automation.
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Boosts safety
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies to scale more easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
Quality products delivered on time
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
Assure compliance with regulations
What are the 4 types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing refers to the transformation of raw materials into useful products by using machines and processes. It includes many different activities like designing, building and testing, packaging, shipping and selling, as well as servicing.
What is the job of a production plan?
A production planner ensures all aspects of the project are delivered on time, within budget, and within scope. A production planner ensures that the service and product meet the client's expectations.
How important is automation in manufacturing?
Not only is automation important for manufacturers, but it's also vital for service providers. It enables them to provide services faster and more efficiently. It reduces human errors and improves productivity, which in turn helps them lower their costs.
What are manufacturing and logistic?
Manufacturing is the process of creating goods from raw materials by using machines and processes. Logistics encompasses the management of all aspects associated with supply chain activities such as procurement, production planning, distribution and inventory control. It also includes customer service. Manufacturing and logistics are often considered together as a broader term that encompasses both the process of creating products and delivering them to customers.
How does a production planner differ from a project manager?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to use lean manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination of defects and waste throughout the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate non-value added activities, such as inspection, work, waiting, and rework.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. For example, Toyota's philosophy underpins its success in automobiles, electronics, appliances, healthcare, chemical engineering, aerospace, paper, food, etc.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow – Ensure that work flows smoothly throughout the process.
-
Standardize & simplify - Make processes consistent and repeatable.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing, although not new, has seen renewed interest in the economic sector since 2008. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. Some economists even believe that lean manufacturing can be a key factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is becoming a popular practice in automotive. It has many advantages. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
Lean manufacturing can be applied to almost every aspect of an organization. Because it makes sure that all value chains are efficient and effectively managed, Lean Manufacturing is particularly helpful for organizations.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM),: ZDM is a system that ensures no defective units are left the manufacturing facility. If a part needs to be fixed during the assembly line, it should be repaired rather than scrapped. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI): CI aims to improve the efficiency of operations by continuously identifying problems and making changes in order to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.